Securing macOS: A Critical Look at Screen Locking Mechanisms.
A screen lock, a fundamental security feature in macOS, is a mechanism that protects user data and access by requiring a password or authentication method upon resuming screen activity after inactivity. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information on a computer. Examples include the automatic lock that occurs after a period of inactivity, or the explicit action of locking the screen via a keyboard shortcut. A correctly configured lock feature ensures a user's work, personal files, or account information are safeguarded against prying eyes.
The importance of screen-locking mechanisms cannot be overstated. They are a crucial component of overall system security. The presence of such features directly correlates to a reduction in the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information. Proactively implementing secure locking strategies contributes to the safety of all user data and intellectual property housed within the device. This is particularly significant in environments where shared or public access to computers is common.
This discussion now delves into the practical application of screen locking in various macOS settings, including the configurations available for customizing lock settings.
macOS Lock Shortcut
A macOS lock shortcut facilitates secure access control. Understanding its components is vital for system protection.
- Keyboard Command
- Inactivity Timer
- Screen Lock Activation
- Password Prompt
- Security Enhancements
- Accessibility Options
- System Integrity
The keyboard command initiates the screen lock process. The inactivity timer automatically engages the lock feature. Activation relies on user input or time thresholds. The password prompt ensures only authorized users gain access. Security enhancements incorporate the lock function into the wider macOS security architecture. Accessibility options accommodate users with disabilities. System integrity is maintained through consistent use of secure locking protocols. For instance, if a user steps away from a shared computer, the inactivity timer triggers the lock, preventing others from accessing the system.
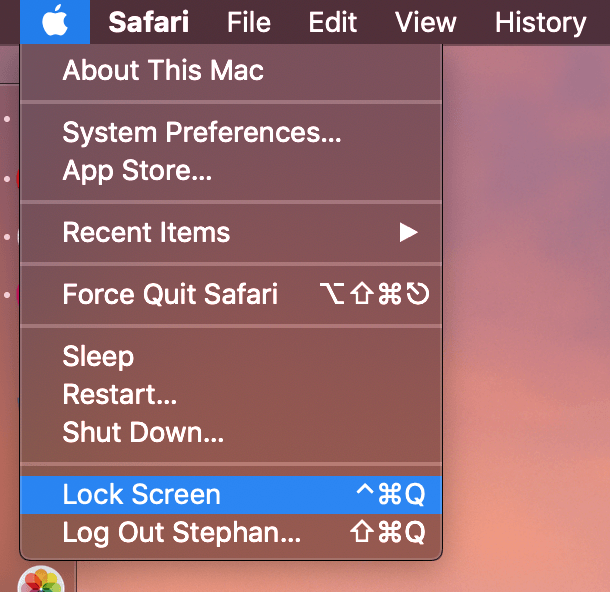
1. Keyboard Command
The keyboard command serves as the crucial trigger for the macOS screen lock. This command, often a combination of specific keys, initiates the security process. Its importance stems from its role as the user-initiated action that immediately implements the screen lock. Without this command, the system would rely solely on inactivity timers, potentially exposing the machine to unauthorized use in certain scenarios.
Consider a user working on a public computer. Using the keyboard command, such as Command + Control + Q, immediately locks the screen, ensuring data protection even if the user briefly steps away. This contrasts with relying solely on an inactivity timer, which might not sufficiently protect information if the user is only momentarily absent. The speed and direct control afforded by a keyboard command significantly enhances security. Moreover, the customizability of keyboard commands allows for flexibility and personalized security settings. The command can be tailored to the user's workflow, enhancing efficiency and ease of use within a secure context.
In conclusion, the keyboard command is a fundamental component of the macOS lock shortcut, providing a rapid and user-controlled method to activate screen protection. Its practical application ensures immediate security, which is crucial in diverse situations, particularly on shared or public computers. Understanding this connection is vital for maintaining data security and preserving system integrity.
2. Inactivity Timer
The inactivity timer is a crucial component of macOS security, directly influencing the functionality of the lock shortcut. Its purpose is to automatically protect the system after a period of user inactivity, preventing unauthorized access.
- Automated Activation
The inactivity timer automatically triggers the lock shortcut when no input is detected from the keyboard, mouse, or other input devices for a specified duration. This automated response ensures consistent security, regardless of user presence or awareness. For example, if a user leaves their computer unattended, the timer initiates the locking process, safeguarding sensitive data during their absence.
- Configuration Flexibility
Users can configure the duration of inactivity that triggers the lock. This configurable aspect of the inactivity timer allows for tailored security settings. A longer inactivity period might be appropriate for a public computer to ensure substantial protection, whereas a shorter period might be satisfactory for a home office computer. This customizable nature makes the timer adaptable to varied scenarios.
- Integration with Lock Shortcut
The inactivity timer's role is integrated with the lock shortcut. The lock shortcut's command-driven activation can also be used, but the timer complements it. When the timer triggers the lock, the system responds by implementing the lock shortcut's security protocols. A key consequence of this interaction is a robust system-wide protection mechanism against potentially harmful events.
- Security Enhancement and User Convenience
By automatically locking the system after a period of inactivity, the inactivity timer enhances the security of the machine and mitigates risks. Conversely, this feature enhances user convenience and efficiency by immediately protecting data when a computer isn't in use. If an unexpected event like a power outage occurs, the data's integrity is safeguarded by the implementation of the lock shortcut when initiated by the inactivity timer.
In conclusion, the inactivity timer and the lock shortcut work in tandem to maintain a high level of system security. The timer's automatic activation, its configurable duration, and its seamless integration with the lock shortcut provide a layered approach to protection. Understanding these mechanics allows users to proactively manage security measures effectively.
3. Screen Lock Activation
Screen lock activation, a core element of macOS security, is intricately linked to the macOS lock shortcut. This process describes how the system transitions from an unlocked to a locked state, safeguarding sensitive information. The specific method of activation, whether triggered by a keyboard shortcut or inactivity, defines the user's interaction with the security mechanism. This exploration examines key facets of this activation process.
- Keyboard Shortcut Activation
The explicit use of a keyboard shortcut directly initiates screen lock activation. This method allows for immediate protection, regardless of inactivity. For instance, pressing Command + Control + Q rapidly enforces the lock. This method is crucial in scenarios requiring immediate security, such as when transitioning between users or leaving a shared computer unattended for brief periods.
- Inactivity Timer Activation
Conversely, screen lock activation can be triggered by the systems inactivity timer. After a predefined period of inactivity, the system automatically initiates the lock procedure. This approach is automatic and protects the system against prolonged unattended use. The timer's configuration controls the sensitivity of the security measure; shorter intervals imply a higher security standard, while longer intervals provide flexibility in user workflow.
- Role of the Password Prompt
Activation, regardless of method, culminates in a password prompt. This crucial element ensures only authorized users can regain access. The password prompt reinforces the security protocol by validating user credentials. This verification step underscores the commitment to data protection.
- System Integration
Screen lock activation is seamlessly integrated into macOS's overall security framework. This integration ensures the functionality aligns with broader security protocols. The seamless connection between activation and other security measures reinforces the robustness of the system's data protection efforts.
In essence, screen lock activation, facilitated by both keyboard shortcuts and inactivity timers, is a cornerstone of macOS's security architecture. The coordinated response, encompassing shortcut activation, the inactivity timer, and the password prompt, ensures a multi-layered approach to data protection. Understanding these components deepens the comprehension of the macOS lock shortcut and its vital function in safeguarding user data and system integrity.
4. Password Prompt
The password prompt is an integral component of the macOS lock shortcut. Its function is to authenticate the user, verifying identity after a screen lock is initiated. This authentication step is crucial in preventing unauthorized access to a user's data and system resources. A password prompt is activated regardless of whether the screen lock is initiated via a keyboard shortcut or an inactivity timer, ensuring a consistent security protocol.
Without the password prompt, the lock shortcut would be significantly less secure. An unauthorized user could potentially circumvent the lock mechanism entirely, gaining access to sensitive files, applications, or account information. Real-world examples of security breaches underscore the importance of such authentication steps. The presence of a password prompt is a primary defense against unauthorized access, confirming the identity of the user before granting continued access to the system. This is essential for maintaining data confidentiality and system integrity. In the case of shared or public computers, the password prompt further enhances security by ensuring only authorized individuals can access the system.
In summary, the password prompt is a fundamental component of the macOS lock shortcut, acting as a crucial security barrier. Its role in verifying user identity and preventing unauthorized access directly impacts the overall security posture of the system. Understanding the connection between the password prompt and the lock shortcut is vital for maintaining system security and protecting sensitive information. This practical knowledge empowers users to make informed decisions about security measures, ultimately strengthening the defenses against cyber threats.
5. Security Enhancements
Security enhancements, encompassing various protective measures, are intrinsically linked to macOS lock shortcuts. These enhancements, interwoven with the lock mechanism, bolster the overall security posture of the system. This examination delves into specific facets of these enhancements, highlighting their interplay with the lock shortcut in securing sensitive data.
- System Integrity Protection (SIP)
SIP, a core component of macOS security, safeguards the operating system from unauthorized modifications. Its integration with the lock shortcut ensures that any attempts to manipulate system files while the system is locked are thwarted. This protects the integrity of the lock mechanism itself, ensuring consistent operation. SIP acts as a fundamental layer of defense, reinforcing the security measures embedded within the lock shortcut.
- File Encryption and Access Control
File encryption and access control mechanisms, crucial for data confidentiality, operate in conjunction with the lock shortcut. The lock shortcut, coupled with these mechanisms, ensures only authorized users can access sensitive data. Encrypted files remain unreadable without the proper authentication provided by the lock shortcut and associated password, enhancing the system's resistance to unauthorized access and data breaches. This combination offers a strong defense against potential threats.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Integration
Two-factor authentication, an additional security layer, can be integrated with the macOS lock shortcut. This feature significantly strengthens security. When combined with the lock shortcut, 2FA adds an extra layer of protection, requiring both a password (protected by the lock shortcut) and a verification code from a separate device (such as a phone). This two-pronged authentication process creates a formidable barrier against unauthorized access attempts, significantly boosting the overall security of the system.
- Software Update Integration
Regular software updates, which are often crucial for patch management, directly influence the effectiveness of the lock shortcut. Updates often incorporate security enhancements that directly impact the reliability and robustness of the lock shortcut. Without consistent updates, security vulnerabilities might arise, potentially compromising the effectiveness of the lock mechanism. The seamless integration between software updates and the lock shortcut forms a dynamic security strategy, adapting to evolving threats and maintaining a robust security posture.
In conclusion, these security enhancements, intricately interwoven with the macOS lock shortcut, contribute to a comprehensive security framework. The combination of these enhancements strengthens the overall protection afforded by the lock shortcut, creating a multi-layered defense against potential threats. This layered approach underscores the importance of a proactive security strategy that encompasses various components and adapts to new security needs.
6. Accessibility Options
Accessibility options, integral to macOS, directly influence the usability and security of screen locking mechanisms. These options are crucial for ensuring inclusivity and equitable access to technology, often requiring modifications to how the lock shortcut functions. Their implementation must be carefully considered to maintain security while accommodating diverse needs.
- Keyboard Shortcuts Customization
Customization of keyboard shortcuts, a fundamental accessibility feature, can significantly impact screen lock activation. Users with physical limitations may require alternative key combinations or input methods. For instance, a user with limited hand mobility might rely on a voice control software to execute the lock shortcut, substituting spoken commands for traditional keyboard inputs. Modifying the default shortcut necessitates careful consideration to avoid unintended consequences and maintain security protocols.
- VoiceOver Integration
VoiceOver, a screen reader, is essential for visually impaired users. VoiceOver's integration with the lock shortcut ensures the user is consistently informed of the status and actions related to the screen lock. This crucial aspect enables the user to understand the process without visual cues. For example, the system could announce "Screen locked" after a specific command has been executed or "Screen unlocked" upon successful authentication with the password. This explicit auditory feedback is essential for navigation and ease of use in the locked and unlocked states.
- Mouse and Trackpad Alternatives
For users with limited or impaired hand function, alternative input methods like voice commands or eye-tracking software might replace traditional mouse or trackpad operations. The lock shortcut must accommodate these alternatives, enabling activation of the screen lock via these alternative methods. This accommodating approach ensures that all users have equal access to the security features of the lock shortcut.
- Screen Magnification Impact
Magnification options, while primarily impacting the visual experience, can indirectly affect the lock shortcut's implementation. Adjusting magnification levels might necessitate modifications to the presentation of the password prompt, ensuring sufficient visibility for users with visual impairments. A well-designed lock shortcut will dynamically scale elements in the password prompt according to magnification levels. This seamless integration ensures the accessibility of the lock function for all users without sacrificing system security.
In conclusion, accessibility options interact intricately with macOS lock shortcuts. Careful consideration of these options ensures equitable access to the functionality without compromising the core security features. The lock shortcut, when designed with accessibility in mind, becomes an integral component of a secure and inclusive user experience, effectively promoting universal access to technology.
7. System Integrity
System Integrity, a core macOS security feature, plays a critical role in safeguarding the operating system's core components. The integrity of these foundational elements is essential to the reliability and security of the macOS lock shortcut. Compromising system integrity can undermine the effectiveness of the lock mechanism, potentially leading to vulnerabilities. Maintaining a robust system integrity framework is crucial for maintaining the security and reliability of the lock feature.
- Protection of Core System Files
System Integrity Protection (SIP) safeguards crucial system files from unauthorized modification. This protection extends to the files directly associated with the macOS lock shortcut, ensuring the integrity of the lock mechanism itself. If unauthorized actors could alter these files, the functionality of the lock shortcut could be subverted, potentially allowing for unauthorized access to the system. This demonstrates a direct link between maintaining system integrity and the effectiveness of the lock feature.
- Mitigation of Malware and Malicious Code
By preventing unauthorized changes to the core operating system files, SIP mitigates the potential impact of malware and malicious code. This is crucial for the integrity of the lock shortcut, as malicious code could exploit vulnerabilities in the system files, ultimately circumventing the security measures embedded within the lock. The secure execution of the lock shortcut depends on a consistently stable and uncompromised system environment.
- Ensuring Consistent Functionality of the Lock Mechanism
System integrity directly influences the reliability of the lock shortcut. A compromised system, where core components have been modified or corrupted, can lead to unpredictable or compromised functionality within the lock mechanism. Malfunctioning authentication protocols, for example, would directly affect the ability to enforce a secure lock, rendering the lock shortcut ineffective. This underlines how system integrity underpins the security offered by the lock feature.
- Maintaining System Stability Through Consistent Updates
A key aspect of maintaining system integrity is regular updates. These updates often address security flaws or vulnerabilities that could be exploited. Consistent updates ensure that any potentially compromising changes are addressed and that the integrity of the macOS lock shortcut is maintained over time. This approach proactively prevents the exploitation of vulnerabilities by maintaining system consistency.
In summary, system integrity is fundamental to the macOS lock shortcut's security. By safeguarding core system files, mitigating malware, ensuring consistent functionality, and enabling reliable updates, system integrity forms a critical pillar in securing the operating system. This directly impacts the reliability and effectiveness of the lock shortcut, underscoring the essential connection between maintaining a secure system and employing effective security mechanisms such as the lock shortcut. A compromised system integrity framework compromises the security that the macOS lock shortcut is designed to provide.
Frequently Asked Questions about macOS Lock Shortcuts
This section addresses common inquiries regarding macOS screen lock shortcuts, providing concise and informative answers to frequently encountered questions. Understanding these aspects is crucial for effective use and security maintenance.
Question 1: What is the default keyboard shortcut for locking the screen in macOS?
The default keyboard shortcut for locking the screen in macOS is Command + Control + Q. This combination immediately activates the screen lock, prompting for a password upon resuming screen activity.
Question 2: How does the inactivity timer work with screen lock shortcuts?
The inactivity timer automatically triggers the screen lock after a specified period of inactivity. This period can be customized within system settings. The timer complements keyboard shortcuts, providing a secondary, automatic locking mechanism when a user is not actively using the input devices.
Question 3: Can I customize the inactivity timer settings?
Yes, the inactivity timer settings can be adjusted. Users can configure the duration before the screen locks, enabling personalized security preferences. These settings are typically found within the System Preferences application.
Question 4: Why is a password prompt essential after a screen lock?
The password prompt is crucial for validating user identity and ensuring only authorized users can access the system after a lock. This authentication step safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Question 5: How do accessibility options affect the implementation of macOS screen lock shortcuts?
Accessibility options, such as VoiceOver, can be integrated with screen lock shortcuts. These options ensure all users, including those with disabilities, can safely and conveniently use the lock feature through alternative input methods. For example, voice commands can trigger the screen lock process.
In summary, macOS screen lock shortcuts employ a combination of keyboard commands and inactivity timers to ensure security. Customization options and accessibility features allow for a user-tailored experience. A properly configured system, employing the lock mechanism and its associated settings, protects sensitive data effectively.
This concludes the FAQ section. The subsequent content explores practical applications of screen lock shortcuts and provides guidance on optimizing security settings for various use cases.
Conclusion
This exploration of macOS lock shortcuts highlights the multifaceted nature of screen security. Keyboard commands and inactivity timers, coupled with password prompts and system integration, form a layered approach to protecting user data. Accessibility options ensure equitable access to these crucial security features, while robust system integrity safeguards the lock mechanism's effectiveness. The article emphasizes the importance of configuring the lock feature to match individual security needs and user workflows. Proper configuration maximizes the security benefits without compromising usability.
Effective use of macOS lock shortcuts is paramount in today's digital landscape. Maintaining a secure environment, whether on personal or shared devices, demands a proactive approach to data protection. The integration of the lock shortcut into daily routines underscores its critical role in safeguarding sensitive information. Understanding these functionalities empowers users to actively manage and enhance their system's security posture. Proactive awareness of these elements contributes to a robust digital environment.
You Might Also Like
Aries Midheaven Leo Rising: Unveiling Your DestinyBest Deals On AZN747 Flights & Packages
Gabby 90 Day Fianc: Latest Updates & Drama!
Nadia Caterina Munno Husband: Who Is He?
Lilly Ghalichi's Husband: Who Is He?
Article Recommendations
- Best Led Qr Codes For Your Project Display
- Augment R Your Aipowered Solution
- 1955 Quarter Value How Much Is Your Coin Worth