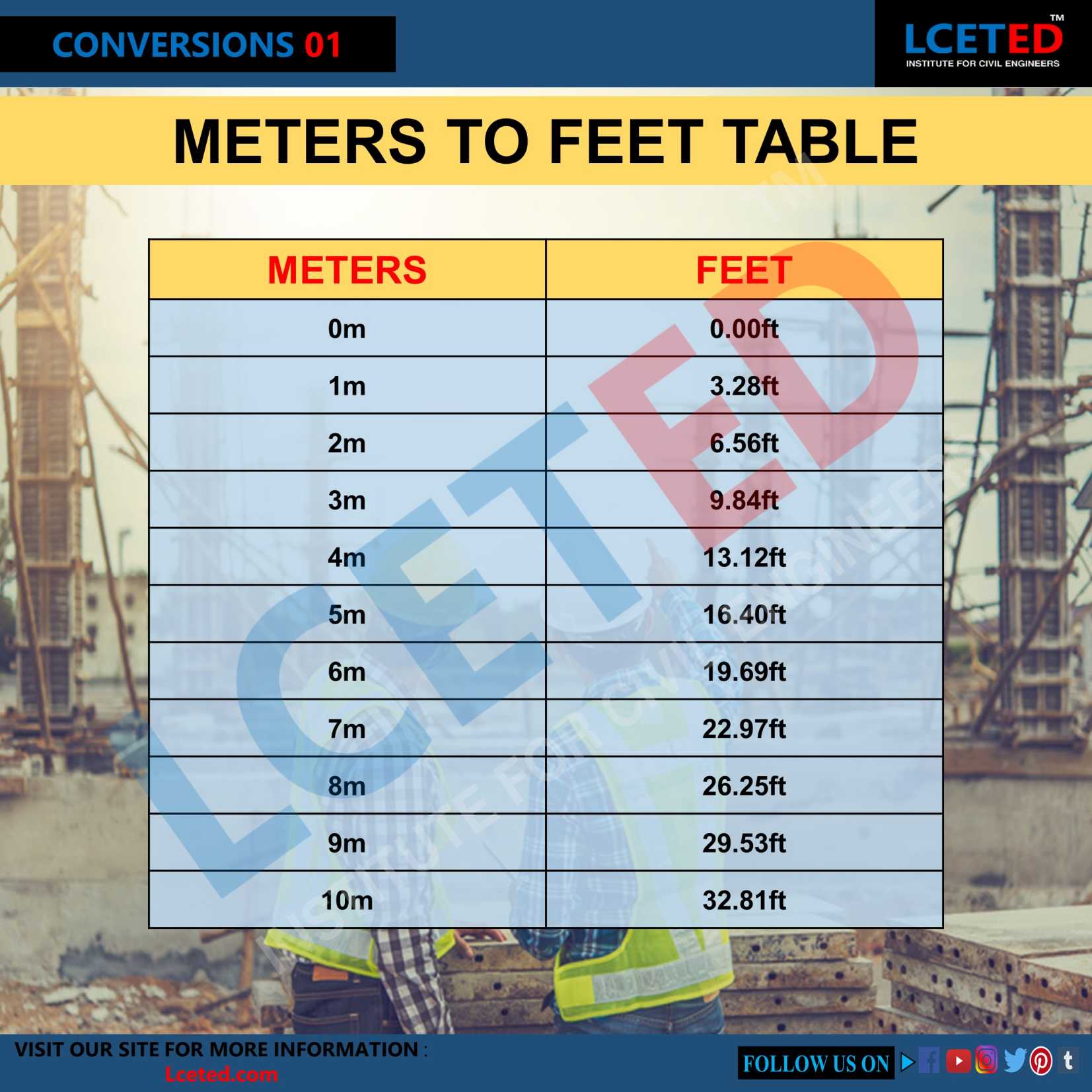
Converting a measurement from meters to feet: A crucial conversion for accurate results.
Converting a measurement from meters to feet is a fundamental task in various fields, including construction, engineering, and design. 1.8 meters represents a specific length. To express this length in feet, one must apply the appropriate conversion factor, recognizing that 1 meter is approximately equal to 3.28084 feet. Therefore, 1.8 meters is equivalent to approximately 5.905 feet. This conversion ensures compatibility between systems of measurement and facilitates precise communication and understanding across various contexts.
This conversion is important because different countries and industries often utilize distinct systems of measurement. Uniformity and consistency in measurements are critical for accurate estimations, calculations, and planning. In construction, for instance, if a design calls for a specific distance of 1.8 meters, knowing the equivalent in feet (approximately 5.9 feet) allows for proper materials ordering and execution on site. Historical context reveals the historical significance of having standardized and interchangeable measurement systems.
This explanation of converting meters to feet focuses on the practical application of such conversions without delving into the personal or biographical details of specific individuals.
1.8m in feet
Understanding the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet is crucial for various applications requiring accurate measurements in different units. This conversion highlights the importance of standardized measurement systems.
- Conversion factor
- Measurement equivalence
- Practical application
- Dimensional analysis
- Accuracy
- Units of measure
- Interchangeability
- Precision
The conversion from meters to feet, as in 1.8 meters, relies on the established conversion factor between the metric and imperial systems. This equivalence is critical for seamless communication and shared understanding in disciplines such as architecture and engineering. Accurate measurements ensure that construction projects, for instance, proceed according to precise specifications. Understanding the units involvedmeters and feetprovides the necessary foundation for applying the conversion. Interchangeability across systems is paramount for ensuring consistency in planning and execution. Dimensional analysis plays a key role in validating calculations, while precision is essential for preventing errors. These factors underscore the importance of accurate measurement conversions for achieving desired results.
1. Conversion factor
A conversion factor is essential for accurately expressing a measurement in different units. In the context of converting 1.8 meters to feet, the conversion factor represents the fixed relationship between the two units. Understanding this relationship is fundamental for accurate calculations and ensuring compatibility across various measurement systems.
- Definition and Application
The conversion factor, in this case, establishes the ratio between meters and feet. It's a numerical value that, when multiplied by the measurement in one unit, yields the equivalent measurement in another. Without this factor, converting 1.8 meters to feet would be impossible. For example, the factor used to convert meters to feet is approximately 3.28084 (1 meter 3.28084 feet). Multiplying 1.8 by this factor results in the equivalent measurement in feet.
- Importance in Accuracy
Accurate conversions are critical in various fields. In construction, an error in converting 1.8 meters to feet could lead to design flaws, material miscalculations, and ultimately, a project that deviates from specifications. Precise conversion ensures the consistency of measurements across projects and across jurisdictions, and this depends on the accuracy of the conversion factor used.
- Maintaining Consistency
Employing the correct conversion factor guarantees consistency in reporting and interpreting measurements. This is vital in fields requiring precise calculations, such as engineering and science. Without consistency, communication and collaboration become difficult. This ensures proper calculations for design parameters and calculations.
- Impact on Practical Applications
The conversion factor is fundamental for practical applications. Interpreting plans, ordering materials, and executing tasks all rely on accurate conversions. If the conversion factor used in converting 1.8 meters is incorrect, then the corresponding measurement in feet will be inaccurate as well. This impacts the entire project or calculation and could create major problems in the process.
In summary, the conversion factor is the cornerstone of accurate conversions between units. Its precise application is imperative for the accurate and consistent results required when converting 1.8 meters to feet, and more broadly in any application that needs to communicate or use measurements that utilize different systems of units.
2. Measurement equivalence
Measurement equivalence forms the bedrock of accurate conversions like determining "1.8m in feet." It signifies the equality of a quantity expressed in different units. In the context of 1.8 meters, this equivalence hinges on the predefined relationship between the meter and the foot, a standardized ratio. This established ratio is crucial, as it ensures consistent understanding and application of measurements across various contexts and disciplines. Without equivalence, discrepancies arise, leading to inaccuracies in calculations and potentially jeopardizing projects or tasks.
Practical examples illustrate the significance of this concept. In construction, precise measurements are paramount. If a blueprint specifies 1.8 meters for a wall length, understanding the equivalent measurement in feet (approximately 5.9 feet) is critical for accurate material ordering and construction. Engineers rely on this equivalence for calculations related to structural integrity, design specifications, and the precise execution of projects. In scientific research, the precise conversion from one unit to another is essential to maintain the accuracy and validity of experimental data. Without this equivalence, inconsistencies and discrepancies could invalidate the findings.
In conclusion, measurement equivalence, as a fundamental concept, underpins accurate conversions like determining "1.8m in feet." Its practical applications highlight the importance of standardized units of measure and the reliable conversion factors between them. Maintaining consistency and accuracy is crucial in various fields, from construction to scientific research, to ensure that projects are completed correctly, and that data are interpreted reliably. Challenges may arise if the equivalence is not understood or applied correctly; these issues can be avoided through thorough understanding and careful application of the principles of measurement equivalence.
3. Practical Application
The practical application of converting 1.8 meters to feet extends beyond a simple mathematical exercise. Accurate conversion is crucial in numerous real-world scenarios where compatibility between metric and imperial units is essential. Precise measurements are fundamental in fields like construction, engineering, and manufacturing. For example, blueprints often utilize metric measurements, while construction materials may be specified in imperial units. A proper conversion is critical for ensuring the design specifications align with the construction process.
Consider a scenario where an architect designs a room with a specific width of 1.8 meters. Without correctly converting this measurement to feet, the contractors may misinterpret the dimensions, leading to inaccuracies in material ordering or the finished product. Similarly, if a manufacturer needs to machine a part with a specified length of 1.8 meters, an incorrect conversion to feet will result in the part not fitting its intended space. In these situations, the accuracy of the conversion directly affects the successful execution of the project. Beyond these direct examples, the conversion underpins many more applications where the interplay of metric and imperial units is a defining factor.
Accurate conversions, including the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet, are vital for effective communication and collaboration across different disciplines and countries. The ability to translate measurements ensures consistency and prevents misunderstandings. Without proper conversion tools and methods, inconsistencies can lead to costly errors, delays, and project failures. Understanding and consistently applying this conversion is paramount for the successful execution of any project involving international cooperation, manufacturing, or construction.
4. Dimensional analysis
Dimensional analysis provides a structured approach to conversions like determining the equivalent of 1.8 meters in feet. It's a crucial component because it ensures consistency and accuracy in calculations involving different units of measurement. The method involves tracking the units of measurement throughout a calculation, ensuring the units align with the desired result.
In the context of converting 1.8 meters to feet, dimensional analysis involves acknowledging the relationship between meters and feet. This relationship is expressed as a conversion factor. A fundamental step is recognizing that 1 meter is approximately equal to 3.28084 feet. This conversion factor, expressed as a ratio (3.28084 feet/1 meter), is essential. To convert 1.8 meters, the calculation employs dimensional analysis. The calculation would proceed by multiplying 1.8 meters by the conversion factor, ensuring that the units "meters" cancel out, leaving the result in feet. Critically, this method ensures the final result incorporates the correct units. Real-world examples include architectural drawings that must translate dimensions from one system to another, ensuring construction accuracy. In manufacturing, it helps guarantee that manufactured components have the precise dimensions dictated by design specifications. Without dimensional analysis, errors in these calculations can have tangible consequences.
In summary, dimensional analysis is indispensable in converting 1.8 meters to feet and, more generally, in any calculation involving multiple units. It offers a structured method to ensure the accuracy and correctness of the results. By meticulously tracking units throughout the calculation, one can avoid errors and ensure that the final result accurately reflects the intended value. This methodical approach is pivotal in various fields relying on precise measurements to prevent substantial inaccuracies and costly errors.
5. Accuracy
Accuracy in converting 1.8 meters to feet is paramount. Inaccurate conversions can have significant consequences in various fields, from construction to engineering. Precise measurements, like the conversion of 1.8 meters, are essential for ensuring projects are completed correctly and meet specifications. Maintaining accuracy throughout the process is vital to prevent errors and ensure the desired outcome.
- Conversion Factor Precision
The accuracy of the conversion hinges on the precision of the conversion factor used. Slight variations in the factor can lead to considerable errors in the resulting measurement in feet. Using a precise and up-to-date conversion factor, like 3.28084 feet per meter, is essential. This precision is particularly critical in fields demanding high levels of accuracy, where minor discrepancies can have major repercussions.
- Minimizing Calculation Errors
Accuracy requires meticulous calculation. Rounding errors in intermediate steps can accumulate, leading to inaccuracies in the final result. Carefully executing the conversion calculation, using appropriate tools or software, minimizes such errors. In situations with strict tolerances, avoiding rounding errors entirely might be necessary, ensuring that every step maintains the desired level of accuracy.
- Contextual Relevance
Accuracy in a conversion like 1.8 meters to feet depends on the context in which it is applied. A slight variance in the final measurement might be inconsequential in a general-purpose measurement, but it could prove critical in applications with strict tolerances. Understanding the specific requirements of the context is essential for selecting the appropriate level of accuracy for the conversion.
- Measurement Tool Calibration
If the initial measurement of 1.8 meters is not accurate, the conversion will be flawed. Using calibrated measuring instruments ensures the initial measurement is precise. Ensuring the reliability of the instruments that provide the original measurement is crucial for the ultimate accuracy of the conversion and the final outcome. If the initial measurement is flawed, the resultant calculation, however accurate in process, will be useless.
Ultimately, achieving accuracy in converting 1.8 meters to feet requires meticulous attention to detail at each stage, from the conversion factor to the initial measurement. The consequences of inaccuracies vary depending on the application, but in all instances, upholding accuracy leads to more reliable and successful outcomes.
6. Units of Measure
Units of measure form the foundation of quantitative expression in various disciplines. The conversion of 1.8 meters to feet exemplifies the crucial role of units in ensuring accurate communication and understanding across different systems. Standardization in units is essential for avoiding ambiguity and misinterpretations, particularly in fields where precision is paramount.
- Metric and Imperial Systems
The conversion from meters to feet highlights the difference between the metric system (based on powers of ten) and the imperial system (often based on historical standards). Understanding the distinction between these systems is fundamental to converting 1.8 meters to feet. The metric system is favored in many scientific and engineering contexts, while the imperial system persists in certain areas, like the United States. Compatibility is achieved through established conversion factors, guaranteeing accurate expression of measurements regardless of the system used. Conversion of 1.8m is dependent on understanding the relationship between these fundamental units.
- Consistency and Accuracy
Maintaining consistent units of measure ensures accuracy in calculations and measurements. Inaccurate conversions, like improperly determining "1.8m in feet," can lead to errors in construction projects, engineering designs, or scientific experiments. Uniformity is critical. Consistency is achieved through rigorous adherence to conversion factors. This prevents ambiguity in any subsequent steps or applications using these measurements, whether in practical or theoretical contexts.
- Conversion Factors and Ratios
Conversion factors establish the relationship between different units. The conversion from meters to feet relies on a precise conversion factor, the ratio between the two units. This factor, which is applied in the calculation, guarantees accurate results and ensures consistent understanding in all applications using either of the two units. Failure to apply the correct factor can lead to inaccurate interpretations, as exemplified by errors in determining "1.8m in feet."
- Practical Applications in Various Disciplines
Units of measure permeate numerous disciplines. In architecture, accurate conversions are essential for construction planning. In engineering, proper unit conversion ensures structural integrity. In manufacturing, units of measure are crucial for product dimensions and ensure compatibility. The need to understand and correctly apply the relationship between different measurement systems is fundamental across many disciplines.
Ultimately, understanding units of measure, including the conversion between meters and feet, as in the example of "1.8m in feet," is essential for accurate communication and reliable outcomes in any quantitative task. Consistency in units guarantees clarity and avoids misinterpretations, ensuring projects proceed according to specifications and calculations remain accurate. The need for accurate conversion factors and adherence to units is paramount across diverse fields.
7. Interchangeability
Interchangeability, in the context of measurements like "1.8m in feet," signifies the ability to express a quantity in different units while maintaining equivalent meaning. This capability arises from the established relationships between these units. The fundamental principle is that a given length, 1.8 meters, represents an identical physical extent regardless of whether it is expressed in meters or feet. Interchangeability ensures that calculations and specifications can be translated across different measurement systems without loss of information or accuracy. This interchangeability is essential for efficient communication and collaboration across disciplines and geographical boundaries.
The practical significance of interchangeability in the context of "1.8m in feet" is demonstrated in diverse applications. In construction, architectural plans might use meters, while material specifications could use feet. Interchangeability enables the seamless conversion between these systems, ensuring that the construction conforms to the design. Similarly, in engineering, designs often use a combination of metric and imperial units. Accurate interchangeability allows engineers to translate and execute these designs correctly. Furthermore, scientific research frequently necessitates conversion between units to ensure compatibility and comparability of data. Interchangeable measurement systems foster collaboration and data sharing among researchers worldwide.
In conclusion, interchangeability is intrinsically linked to the meaningful expression of "1.8m in feet." This ability to convert between units of measurement, founded on established ratios, underpins the effective communication and successful execution of tasks across diverse applications. Ensuring accurate conversion between systems is paramount to avoid errors and ensure compatibility, thereby avoiding potentially significant project delays and costly mistakes. The understanding and application of interchangeability in measurement systems is, therefore, essential for precision and efficiency in countless real-world scenarios.
8. Precision
Precision in converting a measurement like "1.8m in feet" is not merely a matter of convenience; it is fundamental to accurate results in various fields. The conversion itself, though seemingly simple, relies on the precise relationship between the meter and the foot. Any deviation from this precise relationship introduces error. In a construction project, for instance, an inaccuracy in converting 1.8 meters to its equivalent in feet could lead to structural flaws, material miscalculations, and ultimately, a project that fails to meet specifications. The consequences are compounded when considering the interdependence of many elements in a project; one error can cascade into numerous others.
The importance of precision in converting 1.8 meters to feet extends beyond construction. In engineering designs, precise conversions are critical for ensuring mechanical components fit together correctly, and for ensuring safety. Similarly, in scientific experiments, precise measurements are essential for the validity and reliability of results. In medical contexts, minute discrepancies can impact treatments and outcomes. In manufacturing, precision is critical for producing parts with the required dimensions and tolerances. In each case, the precision of the conversion, including "1.8m in feet," impacts the accuracy and effectiveness of the final result. A lack of precision in this seemingly minor calculation can have substantial consequences.
In conclusion, precision in converting 1.8 meters to feet is not merely an academic exercise. It is an essential element in ensuring accuracy and reliability in a wide range of practical applications. From construction to engineering and beyond, the ability to perform precise conversions directly impacts the overall success and safety of projects. Understanding the importance of precision in these fundamental calculations is crucial for achieving the desired level of accuracy in diverse fields. Failure to uphold this standard can lead to significant downstream issues.
Frequently Asked Questions about 1.8 Meters in Feet
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the conversion of 1.8 meters to its equivalent in feet. Accurate conversion is crucial for various applications, particularly in fields requiring precise measurements.
Question 1: What is the approximate equivalent of 1.8 meters in feet?
1.8 meters is roughly equivalent to 5.91 feet. This conversion arises from the established relationship between the metric and imperial systems of measurement.
Question 2: Why is precise conversion important?
Inaccurate conversions, even seemingly minor ones like converting 1.8 meters, can lead to errors in various applications. Inaccurate dimensions in construction, engineering, or manufacturing can result in costly rework, safety hazards, or a failure to meet specifications.
Question 3: How is this conversion calculated?
The conversion is achieved by multiplying the value in meters by the conversion factor. The conversion factor accounts for the relationship between the meter and the foot; 1 meter is approximately equal to 3.28084 feet. This calculation relies on standardized ratios to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Question 4: Are there online tools available to perform this conversion?
Yes, numerous online tools provide straightforward conversion capabilities. These tools often use pre-programmed conversion factors to rapidly calculate equivalent measurements in various units.
Question 5: How can I ensure accuracy in converting 1.8 meters to feet in practical applications?
Employing established conversion factors and verifying calculations are essential. Utilize accurate tools and avoid rounding errors in intermediate steps. Double-checking results and understanding the context of the application are equally important to maintain accuracy.
Understanding the principles behind conversions like 1.8 meters to feet, and applying those principles diligently, is critical for achieving accurate and reliable results in diverse fields.
Moving forward, the next section will explore the historical context behind these measurement systems and their evolution.
Conclusion
The exploration of converting 1.8 meters to feet underscores the fundamental importance of accurate measurement in diverse fields. Key factors, including conversion factors, dimensional analysis, and the precision required in calculations, were highlighted. The inherent relationship between the metric and imperial systems, and the interchangeability between them, was examined, emphasizing the need for consistent application of standardized units. Practical applications, from construction to engineering, demonstrated the critical role of accurate conversions in ensuring projects meet specifications and avoid errors. The analysis revealed that even seemingly simple conversions, like 1.8 meters to feet, hinge on a thorough understanding of underlying principles, meticulous calculation, and the careful application of established methodologies. Errors in these basic conversions can escalate and affect the success of complex projects.
Ultimately, the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet is a microcosm of the broader significance of precise measurements. Understanding and applying the principles discussed here, from conversion factors to dimensional analysis, is crucial for accuracy and reliability in all fields requiring quantitative data. The ability to translate measurements between differing systems ensures that communication, collaboration, and the successful execution of projects are facilitated. Further refinement in the use and application of these fundamental concepts remains crucial for maintaining accuracy in an increasingly complex and interconnected world.
You Might Also Like
7Star HD: Ultimate Streaming Experience!Joe Burrow's Wife: Updates On Her Health
Seth Rollins Ethnicity: A Deep Dive
Doge Unblocker: Bypass Restrictions & Access Now!
HD Hub4u.com: Premium HD Videos & More
Article Recommendations
- Bill Emerson Bridge History Facts
- George Sakellaris Inspiring Stories Insights
- Best Led Qr Codes For Your Project Display