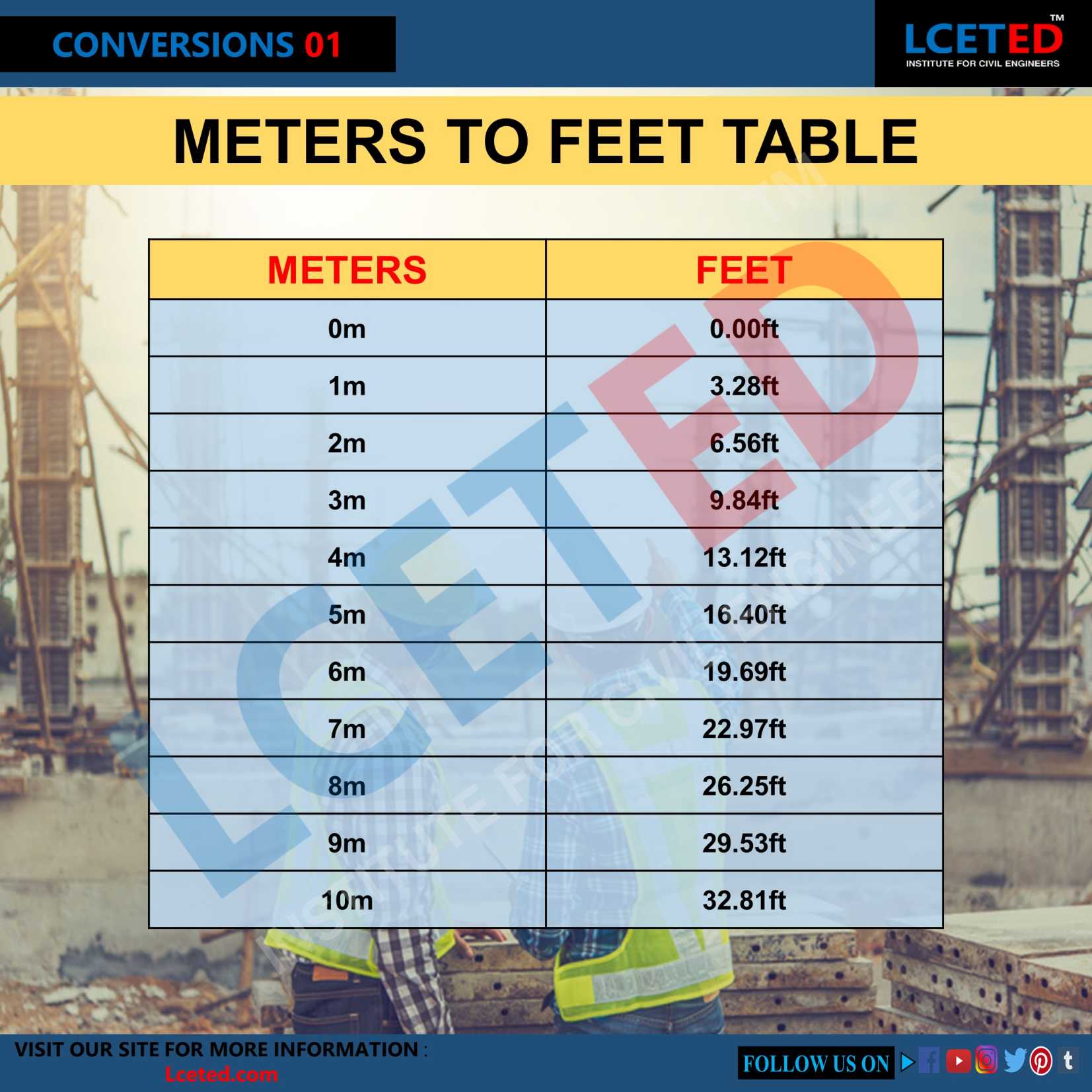
Converting a measurement from meters to feet is a fundamental task in many fields. Understanding the conversion of 1.8 meters to its equivalent in feet is essential for various applications.
Converting 1.8 meters to feet involves a simple calculation using the conversion factor. One meter is approximately equal to 3.28084 feet. Therefore, 1.8 meters is equivalent to 1.8 multiplied by 3.28084 feet, resulting in approximately 5.90551 feet. This conversion is crucial in various contexts, including architecture, engineering, and everyday life.
The conversion's importance stems from the widespread use of both metric and imperial systems. Many countries utilize the metric system, while others predominantly rely on the imperial system. The ability to quickly and accurately convert between these systems is vital for communication and collaboration across diverse settings. This facilitates easy exchange of information and avoids potential errors in various tasks, such as planning construction projects, ordering materials, or understanding technical specifications. Historically, the conversion has been crucial for international cooperation and trade where precise measurements are necessary.
This conversion example demonstrates a common need to interconvert between different measurement units. Further exploration into conversion techniques for other units can be beneficial for a wider range of applications and industries. This provides a broader understanding of units and their relationships, which is a fundamental aspect of many subjects.
1.8m to feet
Understanding the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet is crucial for various applications, from construction to everyday measurements. This conversion involves fundamental units of length and requires a precise understanding of the relationship between the metric and imperial systems.
- Conversion
- Metric system
- Imperial system
- Measurement
- Accuracy
- Units of length
- Equivalence
The conversion of 1.8 meters to feet hinges on the foundational concept of equivalence between units of length. The metric system, based on powers of ten, facilitates straightforward calculations. This conversion exemplifies the importance of accuracy when dealing with units of length in construction, engineering, and other fields requiring precise measurements. Applying the correct conversion factor ensures a precise translation between 1.8 meters and its equivalent in feet, avoiding errors in calculations. Understanding the relationship between these units, including their historical context and practical applications, is vital for accurate measurement.
1. Conversion
Conversion, in the context of measurements, signifies the process of translating a value from one unit of measure to another. This is fundamental in many disciplines, as different systems of measurement (like metric and imperial) are employed globally. The task of converting 1.8 meters to feet directly illustrates this process, demanding an understanding of the relationship between these units.
- Relationship Between Units
Conversion depends on establishing the precise relationship between the units involved. This relationship is often expressed as a conversion factor, a numerical value denoting how many units of one measure are equivalent to one unit of another. For instance, the conversion factor between meters and feet is approximately 3.28084; one meter is equal to approximately 3.28084 feet. Understanding this relationship is crucial for accurate conversions, avoiding errors in calculations.
- Mathematical Foundation
Conversion relies on fundamental mathematical operations, typically multiplication or division. To convert 1.8 meters to feet, the value (1.8) is multiplied by the conversion factor (approximately 3.28084). This mathematical approach applies consistently regardless of the specific values or units involved, making it a standardized procedure across various contexts.
- Practical Applications
Conversion is ubiquitous in numerous real-world scenarios. In construction, architects and engineers routinely convert measurements between metric and imperial systems. In scientific research, consistent units are imperative for accurate data analysis. Even everyday activities, such as following a recipe or using a foreign map, necessitate unit conversion.
- Accuracy and Precision
The accuracy of a conversion directly impacts the reliability of results. Care must be taken when dealing with conversion factors. Using a rounded value might yield an acceptable, but not exact, result. Employing more precise conversion factors enhances accuracy, particularly in situations with strict tolerances, such as engineering or manufacturing.
In summary, the act of converting 1.8 meters to feet exemplifies the broader process of conversion. It highlights the importance of clear relationships between units, accurate calculations, and practical application in various fields where precision is paramount. Conversion is not limited to this one example but rather is a universal process applicable across numerous measurement systems and applications.
2. Metric system
The metric system, a decimal-based system of measurement, underpins the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet. Its standardized units and consistent relationships facilitate precise calculations, crucial in various fields relying on accurate measurements. Understanding the metric system's structure is essential to comprehending the conversion process.
- Fundamental Units
The metric system's cornerstone is a set of fundamental unitsmeter for length, kilogram for mass, and second for time. Derived units, like the square meter for area, are built from these fundamentals. The standardized nature of these units provides a universal language for expressing measurements across disciplines. This standardization simplifies conversion calculations, as the relationships between units are consistent and well-defined.
- Decimal Relationships
Decimal relationships form the backbone of the metric system. Subdivisions and multiples of units are represented by prefixes like milli-, centi-, deci-, kilo-, and so forth. For instance, a kilometer is 1000 meters. This hierarchical structure allows for easy conversions between units by employing factors of ten, as exemplified in converting meters to centimeters. The consistent decimal relationship directly impacts the calculation of 1.8 meters to feet.
- International Adoption
The metric system's widespread adoption facilitates international communication and collaboration. Its universal application eliminates ambiguities often encountered in systems using diverse units. This standardization is critical for fields requiring precise measurements, like engineering, scientific research, and manufacturing. Conversion between different systems, like the conversion between metric and imperial units, becomes necessary when dealing with global projects or data.
- Conversion Factors
Conversion between the metric system and other systems like the imperial system involves precise conversion factors. These factors represent the proportionality between the units. In the case of converting meters to feet, a specific factor relates the two units. This understanding of conversion factors is fundamental for accurate calculations in all metric-based measurements, including the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet.
In conclusion, the metric system's inherent structure of standardized units, decimal relationships, global adoption, and conversion factors is foundational for the accurate conversion of 1.8 meters to feet. Understanding these principles is not limited to a single conversion but is fundamental to a wide range of measurements and applications.
3. Imperial system
The imperial system, a system of measurement rooted in historical British units, presents a contrasting perspective to the metric system when considering conversions like 1.8 meters to feet. Understanding the imperial system's structure is essential for interpreting and applying measurements within its framework and for appreciating the differences in approach between measurement systems.
- Fundamental Units
The imperial system relies on units like feet, inches, yards, and miles for length. These units are not inherently tied to a decimal system. Conversion between these units often involves fractions and different scales, distinguishing it from the consistent decimal structure of the metric system. This difference directly impacts the way conversions between systems are calculated.
- Historical Context
The imperial system's units originated from historical practices and measurements, often linked to the physical world and human-scale activities. The development of units like the foot, initially related to the human foot, highlights the historical nature of the system's construction and units. This historical context offers a distinct perspective on units of measure compared to the metric system, which is fundamentally based on decimal units.
- Conversion Challenges
Conversion between the imperial system and other systems, like the metric system, requires careful attention to conversion factors. These factors are not as readily apparent or consistent with powers of ten as in the metric system. The calculation required to convert 1.8 meters to feet, for instance, involves a specific numerical relationship between the units in the two systems, a facet not inherent in internal imperial system conversions.
- Global Application
While the metric system is now predominantly used internationally, the imperial system remains relevant in some countries and for particular industries. Understanding these diverse measurement systems allows for effective communication and comprehension across global contexts. For instance, some technical documents or drawings in certain sectors might still use imperial units, requiring the ability to interpret these values.
The imperial system's historical underpinnings, the reliance on non-decimal conversion factors, and its continued use in certain contexts all influence the interpretation and calculation of measurements. Understanding this system is important for comparing and converting values across systems, including the conversion of 1.8 meters to its equivalent in feet within the imperial system. The different approaches and structures of each system offer valuable insights into diverse approaches to measurement.
4. Measurement
Accurate measurement is fundamental to countless applications, from architectural design to scientific research. The conversion of 1.8 meters to feet epitomizes this concept, highlighting the necessity of precise relationships between units of measure. Understanding the components of measurement and their implications is crucial for avoiding errors in various contexts.
- Units of Measure
Different systems of measurement exist, each employing unique units. The metric system, based on powers of ten, facilitates straightforward conversions, while the imperial system, rooted in historical units, necessitates more complex conversions. The conversion from meters to feet represents the transition between these systems, highlighting the need for a clear understanding of the specific units involved and their relationships.
- Conversion Factors
Accurate conversion relies on established conversion factors. The relationship between meters and feet is represented by a specific numerical value, which dictates how many units of one measure correspond to another. Employing the correct conversion factor ensures the accuracy of the conversion from 1.8 meters to its equivalent in feet. The selection and application of the correct factor are essential for achieving precise results.
- Accuracy and Precision
The level of accuracy required varies significantly depending on the application. In some cases, a rough estimate might suffice, but precise measurements are crucial in fields like engineering and construction. The conversion of 1.8 meters to feet demonstrates that even small discrepancies in conversion factors can lead to significant errors in final calculations, emphasizing the importance of precision in measurements.
- Contextual Application
The context surrounding a measurement profoundly influences its interpretation and use. Whether determining the dimensions of a room, calculating the speed of an object, or analyzing data, the specific context provides the framework for meaningful interpretation of the numerical results derived from a measurement. The conversion from 1.8 meters to feet necessitates an understanding of the context in which this value is being used.
In essence, the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet underscores the multifaceted nature of measurement. It requires an understanding of the units involved, the necessary conversion factors, the degree of accuracy demanded, and the context of application. Accurate measurement is critical for avoiding errors and ensuring that calculations and interpretations are meaningful and reliable.
5. Accuracy
The conversion of 1.8 meters to feet, while seemingly straightforward, hinges on accuracy. Inaccurate conversion factors or calculations can lead to significant discrepancies, especially in applications requiring precision. This exploration examines the critical role of accuracy in such a conversion.
- Conversion Factors and Their Precision
The conversion between metric and imperial units relies on established conversion factors. Using an approximate value instead of the precise conversion factor (approximately 3.28084 feet per meter) introduces error. The magnitude of this error will depend on the specific application and the desired level of accuracy. In scenarios requiring precise measurements, such as engineering or construction, employing a less precise conversion factor can lead to critical errors in final calculations.
- Mathematical Operations and Rounding
Calculations involving conversion factors often necessitate multiplication and subsequent rounding. The precision of the result is directly impacted by the level of precision in the initial conversion factor and by the rounding approach used. Rounding to a certain number of decimal places can introduce errors if not handled with care. For instance, rounding 5.90551 feet to 5.9 feet for general purposes may be acceptable; however, for detailed engineering work, the extra decimal places provide critical data accuracy.
- Application Context and Required Precision
The required degree of accuracy for a conversion varies greatly depending on the application. A casual measurement, such as determining the length of a tabletop, may tolerate a lower degree of precision. However, the precise conversion of 1.8 meters is critical when designing a building or a piece of machinery, where even minor variations in length can compromise functionality or structural integrity. Understanding the application context is paramount in determining the acceptable margin of error.
- Minimizing Errors Through Tools and Techniques
Employing appropriate tools and adhering to established procedures can enhance the accuracy of conversions. Specialized calculators and conversion software often offer higher precision. Rigorous adherence to standardized procedures and protocols in measurement ensures consistent accuracy and reduces inconsistencies. The careful selection and use of these tools play a key role in minimizing errors associated with the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet.
Ultimately, maintaining accuracy in converting 1.8 meters to feet, or any other measurement conversion, requires awareness of conversion factors, mathematical operations, the application's sensitivity to precision, and the use of appropriate tools and techniques. Compromising on accuracy can have significant consequences, particularly in situations where precise calculations are critical.
6. Units of Length
Units of length form the bedrock of all measurements involving distance. The conversion of 1.8 meters to feet directly illustrates this principle. Understanding the relationship between different length units is crucial, as errors in their application can lead to significant inaccuracies in various fields, including engineering, construction, and even everyday activities. The choice of units whether meters or feet directly impacts calculations and interpretations.
The conversion from meters to feet necessitates recognizing that a meter and a foot represent distinct lengths. A meter is a standardized unit within the metric system, based on decimal increments. Conversely, a foot is a unit within the imperial system. Direct conversion requires understanding the established ratio between these units. The fundamental connection lies in the need to express a single physical dimension using consistent units for meaningful interpretation and calculation. For instance, if a blueprint for a house is drawn in feet, all measurements must consistently adhere to the foot unit; otherwise, dimensional accuracy is compromised. This impacts the accurate portrayal of the house's features and, ultimately, its construction.
In summary, units of length are fundamental to measurement. The conversion from 1.8 meters to feet, or any similar conversion, highlights the importance of accurately recognizing and applying appropriate units. This recognition isn't merely an abstract concept; it directly impacts practical applications and real-world outcomes. Choosing the correct unit of length dictates the precision of calculations and the reliability of the resulting information.
7. Equivalence
The concept of equivalence is central to the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet. It establishes a fundamental relationship between two seemingly different units of measurement. Understanding this relationship is critical for accurate calculations and meaningful interpretation of dimensions in various fields.
- Definition and Application
Equivalence, in the context of measurement, signifies that two distinct units represent the same physical quantity. This means 1.8 meters precisely corresponds to a specific length in feet. This correspondence allows for the translation of a measurement from one system to another. For example, a 1.8-meter-long object is equivalent to a specific length measured in feet.
- Mathematical Representation
The equivalence between 1.8 meters and its corresponding feet is expressed mathematically through a conversion factor. This factor quantifies the relationship between the units. In this case, the conversion factor links meters to feet, allowing for the mathematical calculation of the equivalent length. This conversion factor is crucial for translating measurements between the metric and imperial systems, ensuring consistency in different contexts.
- Importance in Practical Applications
Equivalence is essential in numerous practical applications. In construction, architects and engineers often need to convert measurements between metric and imperial units. This ensures consistency in blueprints, design specifications, and ultimately, the construction process. Equivalence is similarly important in scientific research and manufacturing, where standardized measurements are vital for accurate data analysis and consistent production.
- Contextual Significance
The notion of equivalence is not just about mathematical calculations; it underscores the physical reality that a specific length remains unchanged despite being expressed in different units. This consistency is critical for accurate communication and avoids errors in diverse fields, especially where precision is paramount. Understanding the equivalence between 1.8 meters and its equivalent in feet is essential for avoiding inaccuracies and ensuring that measurements are consistent and meaningful in practical applications.
In conclusion, equivalence between 1.8 meters and its representation in feet, through a conversion factor, is not merely a mathematical exercise; it represents a fundamental principle in measurement. This concept ensures consistency in diverse applications, allowing for accurate communication, efficient collaboration, and reliable results across various fields. Understanding this equivalence ensures correct interpretation and utilization of measurements across different contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (1.8m to Feet)
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet. Clear and concise answers are provided to facilitate understanding of this conversion process.
Question 1: What is the precise conversion of 1.8 meters to feet?
The precise conversion of 1.8 meters is approximately 5.90551 feet. Using a rounded value, such as 5.9 feet, may suffice for general purposes. However, employing a more precise value is essential in applications requiring high accuracy, such as engineering or construction.
Question 2: Why is it necessary to convert between meters and feet?
Conversion between units, like meters and feet, is essential for seamless communication and collaboration across diverse settings. Different countries and industries employ varying systems of measurement. Conversion ensures that information is readily understandable and applicable regardless of the measuring system used.
Question 3: What is the underlying relationship between meters and feet?
A meter is a unit in the metric system, while a foot is a unit in the imperial system. The conversion hinges on a defined relationship between these units. One meter is approximately equal to 3.28084 feet.
Question 4: How can I ensure accuracy during conversions?
Accuracy in conversion relies on using the precise conversion factor and careful execution of mathematical operations. Employing accurate conversion factors and employing precise calculations minimizes errors. Using appropriate tools, such as calculators or conversion software designed for such conversions, can further enhance accuracy.
Question 5: What are some practical applications of this conversion?
This conversion is fundamental in various applications, including architectural design, engineering, scientific research, and everyday measurements. Converting between systems ensures that dimensions are accurately represented and applied in projects using different measurement systems.
Understanding the conversion of 1.8 meters to feet is crucial for effectively utilizing and interpreting measurements in a variety of contexts, particularly in fields demanding precision.
This concludes the FAQ section. The next section will delve into detailed calculations for further exploration.
Conclusion
This exploration of converting 1.8 meters to feet underscores the fundamental importance of accurate unit conversion. The process hinges on a precise understanding of the relationship between the metric and imperial systems, requiring careful application of conversion factors. Key aspects highlighted include the mathematical underpinnings of the conversion, the historical context of measurement systems, and the crucial role of accuracy in diverse applications, ranging from construction to scientific research. The exploration reveals that seemingly simple conversions, like 1.8 meters to feet, necessitate a thorough grasp of underlying principles for reliable outcomes. Accurate measurements are foundational in myriad disciplines, and this conversion serves as a concise example of the critical need for precision in calculations and interpretation of data.
The conversion of 1.8 meters to feet, while seemingly straightforward, highlights the significance of consistent and precise methodologies in all forms of measurement. Reliable conversion hinges on a thorough understanding of units, conversion factors, and the specific context of application. Maintaining accuracy is not just a procedural step but a critical element in ensuring consistent results across different fields and applications. Further exploration of measurement principles and their diverse applications is essential for continued progress in areas demanding precise and reliable data.
You Might Also Like
Mercedes Schlapp Facelift Surgery: Expert Procedures & ResultsMasa49 Me: Exclusive Deals & Offers
Best Hub4u Movies & Shows: Streaming Now!
HD Hub4You: Premium HD Videos & Entertainment
Tony Heidi Kill: Shocking News & Update!
Article Recommendations
- George Sakellaris Inspiring Stories Insights
- 1955 Quarter Value How Much Is Your Coin Worth
- Augment R Your Aipowered Solution